Centre for Materials Science & Culture Resources
Jump to
Here you will find a selection of Resources created by the Centre for Materials Science & Culture designed for use by designers and businesses who are looking to improve on the sustainability of their processes.

Textiles Circularity Centre resources
Developed as part of the UKRI Textiles Circularity Centre, the following resources, divided into the three research themes of Materials Circularity, Consumer Experience and Circular Supply Chain, were designed to enable designers and brands to move towards more circular practices.
Materials Circularity Resources
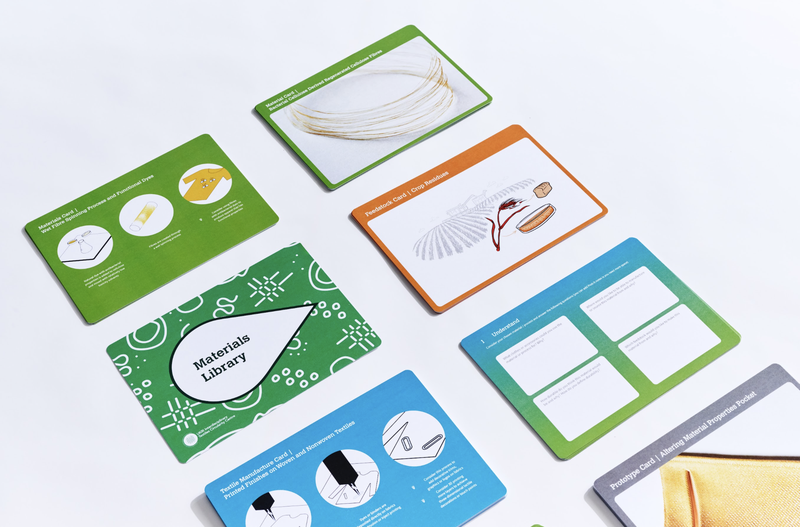
Materials Library
The Materials Library helps designers understand and use circular materials and advanced manufacturing technologies to transform their business and practice. The library consists of cards that show the range of materials and manufacturing processes we have developed. They include fibres, yarns, textiles and finishes that can be used to add value to waste.
The library includes:
- orange coloured cards that show feedstocks of the waste we use to make bacterial cellulose-based materials
- green coloured cards showcasing prototypes of materials with illustrations of design possibilities
- blue coloured cards illustrating the manufacturing processes of the materials detailed on the green cards, as well as materials that do not exist yet at scale
- grey coloured cards with prototypes showing the possibilities of how the materials created could be applied in the design of circular products

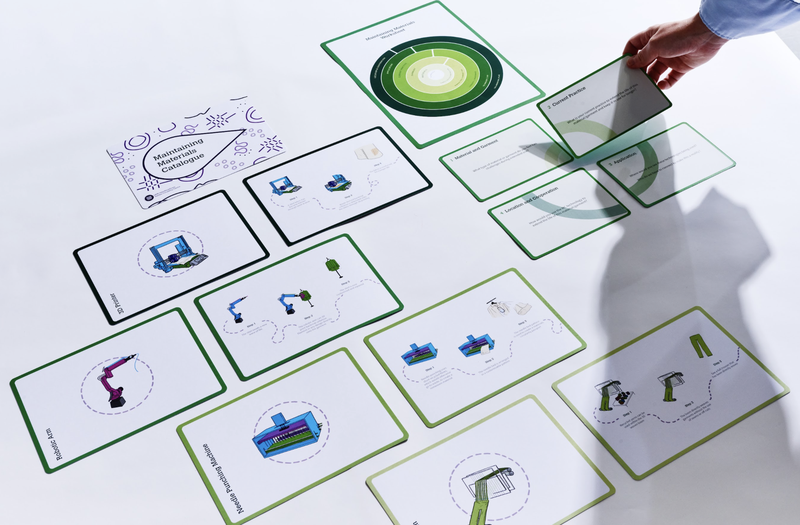
Maintaining Materials Toolkit
The Maintaining Materials (M2) Toolkit demonstrates how advanced fabrication technologies can be redesigned so that they can be used to extend the life of materials already in use. We propose using our circular textile fabrication technologies beyond simply the production of textiles, but also throughout the use phase to extend their lifespan.
These fabrication technologies include:
3D printer and 3D robotic arm: 3D printing is a versatile technique for depositing bio-based materials onto specific locations. We use this technique for repair by printing bio-based materials directly onto garments and production of textile composites.
Bespoke needle-punching machine: fine-gauge barb needles developed to integrate bacterial cellulose with short recycled fibres that are otherwise unable to be spun into yarns. We use this technique to reinforce products through a recycled textile substrate suitable for garment use.
3D weaving loom: a digital manufacturing technology to seamlessly produce bespoke garments with significantly reduced process wastage, production lead-time and touch-time. Unlike traditional methods that involve cutting and stitching flat fabrics, we use this technique to create functional elements, reduce fabric waste, simplify production, and enhance the durability and comfort of garments.
Consumer Experience Resources
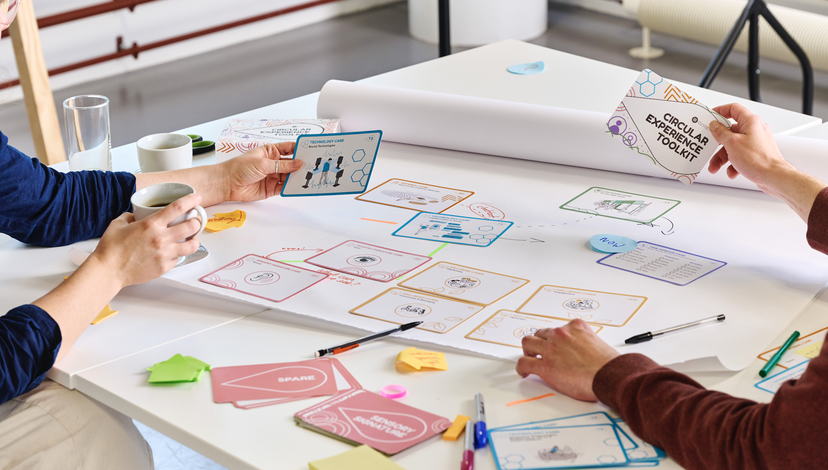
Circular Experience Toolkit
The Circular Experience Toolkit is a design resource that supports fashion professionals to develop retail experiences and services that engage consumers in the circular textile economy.

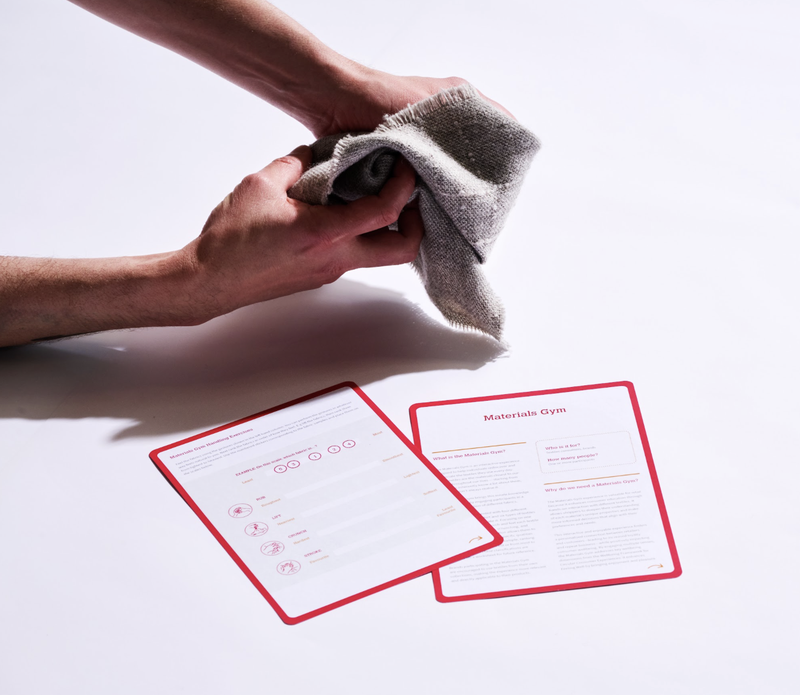
Materials Gym
The Materials Gym is an interactive experience designed to help consumers realise what they know about textiles and learn how to express and use this knowledge. Since textiles are the materials closest to our bodies throughout our lives, we inherently know a lot about them, even if we don't always realise it. The Materials Gym brings this knowledge to the fore by engaging participants in a guided hands-on exploration of different fabrics.

Circular Shirt Builder
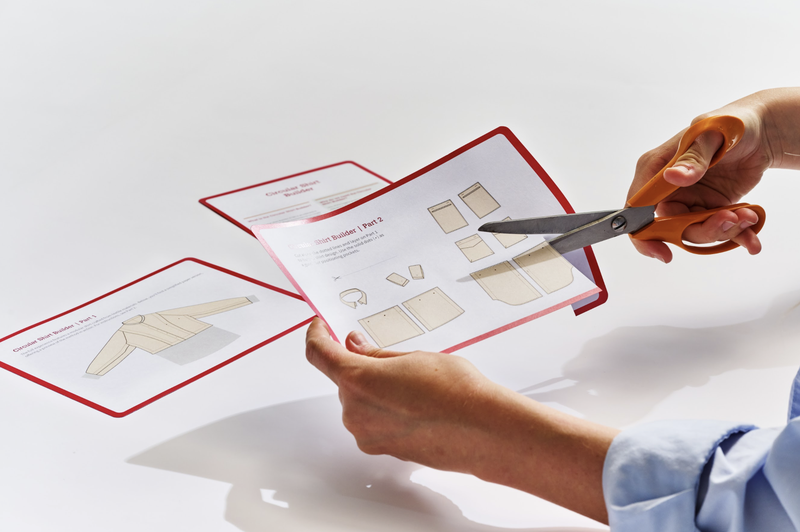
The Circular Shirt Builder is a physical configurator where consumers can customise and assemble a modular shirt featuring interchangeable components such as collar styles, sleeves, and front and back panels. It is a research platform to investigate co-design as a strategy to embed circular principles in consumer behaviour, encouraging them to view garments as long-term, adaptable investments rather than disposable items.

Biofibre Explorer
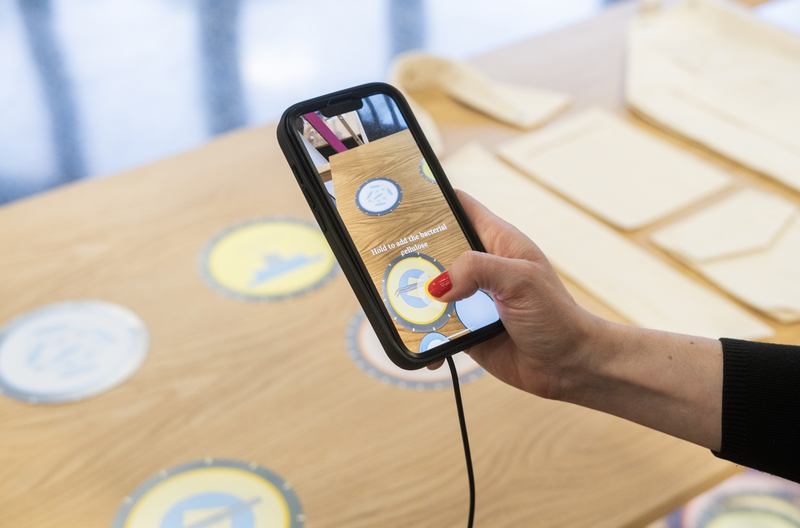
The Biofibre Explorer is an Augmented Reality tool that makes learning about bio-based textiles an engaging and playful experience. It offers an interactive, step-by-step demonstration of the wet spinning process used to create cellulose-based textiles. Through Augmented Reality, consumers can have a multisensory immersion in the materials' origins and potential fashion applications. It facilitates learning and invites users to envision their future-selves participating in more informed and healthy consumption behaviour. Features like phone vibrations enhanced physical involvement and immersion. By demonstrating the effort and innovation behind biobased materials, the tool deepened the emotional connection to these materials.

Circular Supply Chain Resources
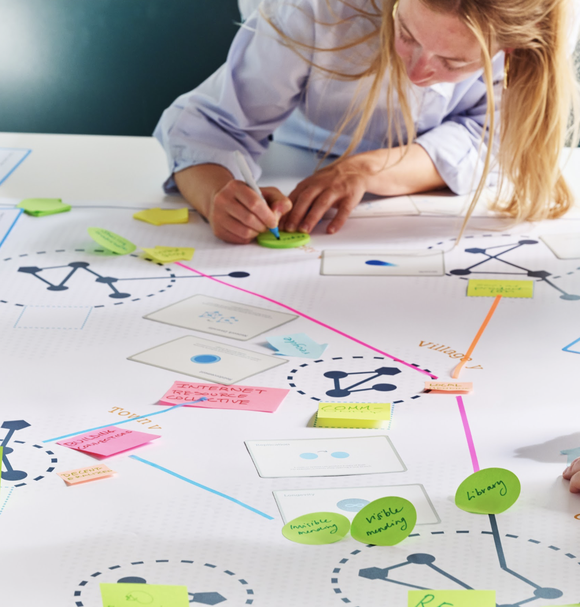
Circular System Design Tool
The Circular System Design Tool is an approach to mapping interactive networks of people, things and places that facilitate circular flows of clothing in the hyper-local economy of a town. It also allows us, system actors, to evaluate our local supply chains in order to successfully support our behaviours through the layering of different elements on a large blueprint.
System of Systems Design Tool
The System of Systems Design tool is particularly useful to identify how individuals and collectives can leverage their existing relationships and establish new connections or system conditions for expanding the system and cooperation across regions to make supply chains more sustainable and resilient. As the goal is to maximise value while keeping clothes in circulation for longer, towns and cities can support each other by harnessing the strengths and specialisms of the individuals who live there whether they are designers, apparel brands, repairers, upcyclers, recyclers, manufacturers or biomaterial brewers.
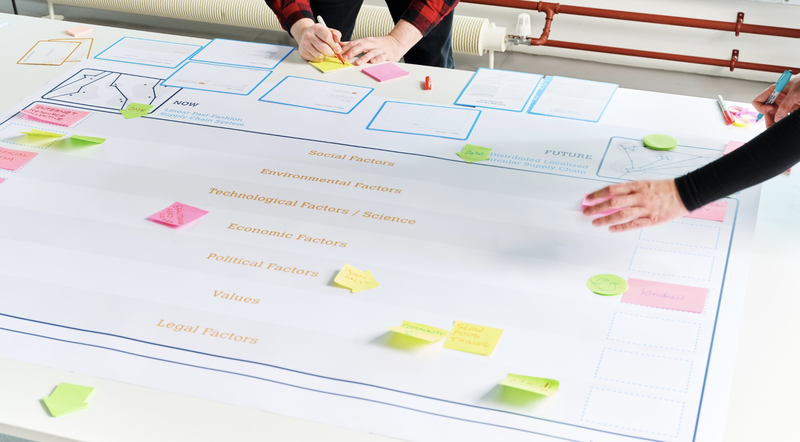
Futuring Circular Systems Tool
The Futuring Circular Systems guides the mapping of interrelated influencing factors on a pathway to an alternative reality. We used the tool to build pathways between:
The Now: a linear fast-fashion supply chain, characterised by the UK apparel-textile sectors operating in a global system whereby mass production, overconsumption and resource intensive processes cause environmental degradation
And the Future: a preferable scenario where Social Production Networks are a norm in the UK – a distributed circular supply chain, characterised by UK-based communities operating in resilient supply chains, where distributed manufacture, repair, care, reuse, etc., support a system of regenerative fashion.
Want to learn about how our tools can support your move towards circularity?
msrc@rca.ac.uk
